Audio
The audio solution of the Hiber3D engine is based on the C++ audio library SoLoud .
Audio components
Audio, similar to much of the rest of Hiber3D, is interfaced through ECS, meaning that the way to set-up audio in your project is done by creating components.
AudioSource
To add play an audio asset in your scene, either through the editor or code, first add an AudioSource component to an entity in the scene.
This can be done either through the editor:
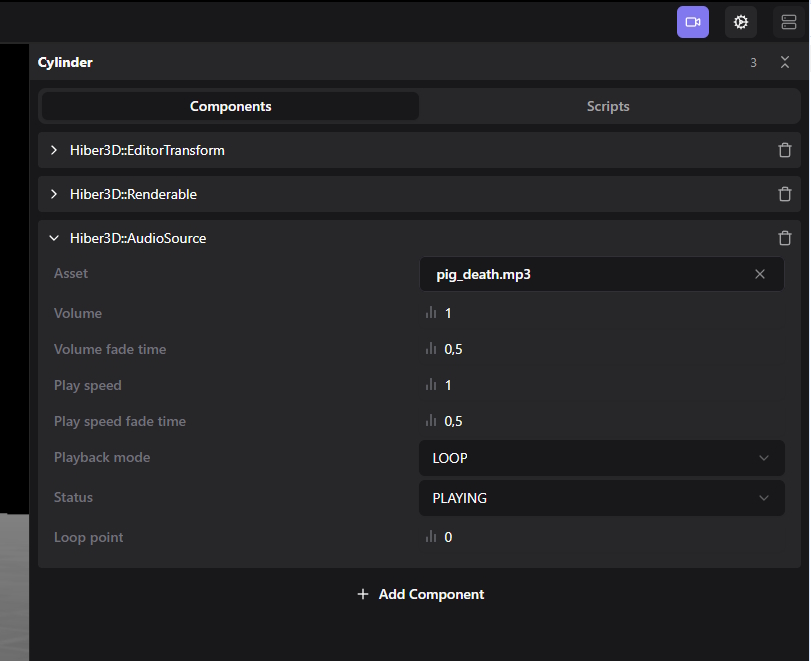
Or in scripting:
const audioEntity = hiber3d.createEntity();
hiber3d.addComponent(audioEntity, "Hiber3D::AudioSource");
hiber3d.setComponent(audioEntity, "Hiber3D::AudioSource", "asset", "my_audio_asset.mp3");
...Or in C++:
const auto audioEntity = registry.create();
auto& audioSource = registry.emplace<Hiber3D::AudioSource>(audioEntity, {})
...SpatialAudio
The SpatialAudio component is used together with AudioSource to create 3D sounds.
If creating this component programatically, create it before the AudioSource component, as sounds already playing cannot be transformed into 3D sounds.
In order for 3D audio to work, you also need an AudioListener component, the “microphone” of the game. You will most likely want the AudioListener component on the same entity as the Camera component.
Just like Camera components, you can have as many AudioListener components as you like, but only one of them will be active at any time. The engine will choose the one with the highest priority.
The SpatialAudio component has a number of settings for how the volume of the audio should change as the distance changes.
Note that the minimum and maximum attenuation distances define the range in which the volume changes based on the distance, not the range in which audio is audible at all.
As long as the distance is lower than the minimum attenuation distance, the volume will be the one defined in the AudioSource component.
In the range between the minium and maximum attenuation distance, volume will decrease as the distance increases.
When the distance is higher than the maximum attenunation distance, volume will no longer be decreasd as the distance increases. Exceeding the maximum attenuation distance does not necessarily mean that the audio is silenced.
For more details on the attenuation models, see https://solhsa.com/soloud/concepts3d.html